Will make you easily discover how does AI work?
Do you want to know how does AI work? Have you ever wondered how artificial intelligence achieves its so-called intelligence? What goes into making software, machine, or systems to possess human-like thinking and decision-making capabilities to analyze and interpret data? What underlying methods or techniques do these systems employ to accomplish such a task?
In the previous post, which you can read here, we touched upon the basics of artificial intelligence topics, especially what is Artificial Intelligence (AI), the history of AI, the types of AI, why AI is so useful, and the future of AI.
In this post, we will go through the basics of how does AI work? The sub-fields of AI, AI in our everyday life, the goals of AI, the purpose of AI, and other essential topics of AI. So, let’s start to figure out what comes under the “Artificial Intelligence” umbrella.
Table of contents:
Highlights:
- Artificial intelligence, in the form of machine learning, empowers software programs to predict possibilities more reliably without having to be deliberately designed.
- A neural network is a kind of machine learning that comprises connected, information-processing nodes (similar to neurons) that adapt to outside information and interact with one another.
- A computational model can be trained to do classification tasks using deep learning using data such as photos, text, or sound.
- Computer vision uses deep learning and pattern recognition to identify what is present in a photo or video.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) examines, comprehends, and produces written or audio answers based on the natural languages that people speak.
- Artificial intelligence’s purpose is to complement human abilities and assist us in making complex decisions that have broad implications.
How does AI work?
Just for a quick recap, Artificial Intelligence is the ability of a digital computer or computer-controlled robot to perform tasks commonly associated with intelligent beings.
An extensive volume of labeled training data is processed by AI systems which further evaluate the data for any relationships and similarities before applying these similarities to anticipate potential future states.
This same technique is used in image analysis software that can begin to recognize and interpret things in photographs by analyzing millions of samples.
A chatbot that is provided samples of textual conversations and then figures out how to make authentic interactions with humans.
A stock trading tool that is trained by millions of past data makes predictions of the share market in the future.
Three stages of how does AI work?
Three intellectual abilities: learning, reasoning, and self-correction—are the key themes of an AI program.
Learning Ability: The learning ability part of AI technology is associated with collecting information and constructing the procedures that will enable the information to be processed into useful knowledge. These procedures, also known as algorithms, give computational systems specific instructions on how to carry out a particular activity.
Reasoning Ability: The Reasoning ability part of AI technology deals with selecting the most appropriate algorithm to accomplish a specific result.
Self-correcting Ability: This part of AI technology is responsible for continuously improving algorithms making sure they deliver the most precise results.
Reverse engineering of human characteristics and talents into a machine and employing its computing capacity to go beyond what we are skillful at, is the methodical process of developing an AI system.
For the software to learn independently from similarities or attributes in the data, artificial intelligence (AI) combines enormous amounts of information with speedy, iterative processing and sophisticated algorithms.
For the development and training of machine learning algorithms, AI requires a platform of sophisticated equipment and software. There is not one programming language that is affiliated with AI, but a handful is, including R, Python, and Java.
Understanding the numerous sub-fields of artificial intelligence and how those fields may be applied to different areas of the industry requires a deep dive into how the technology operates.
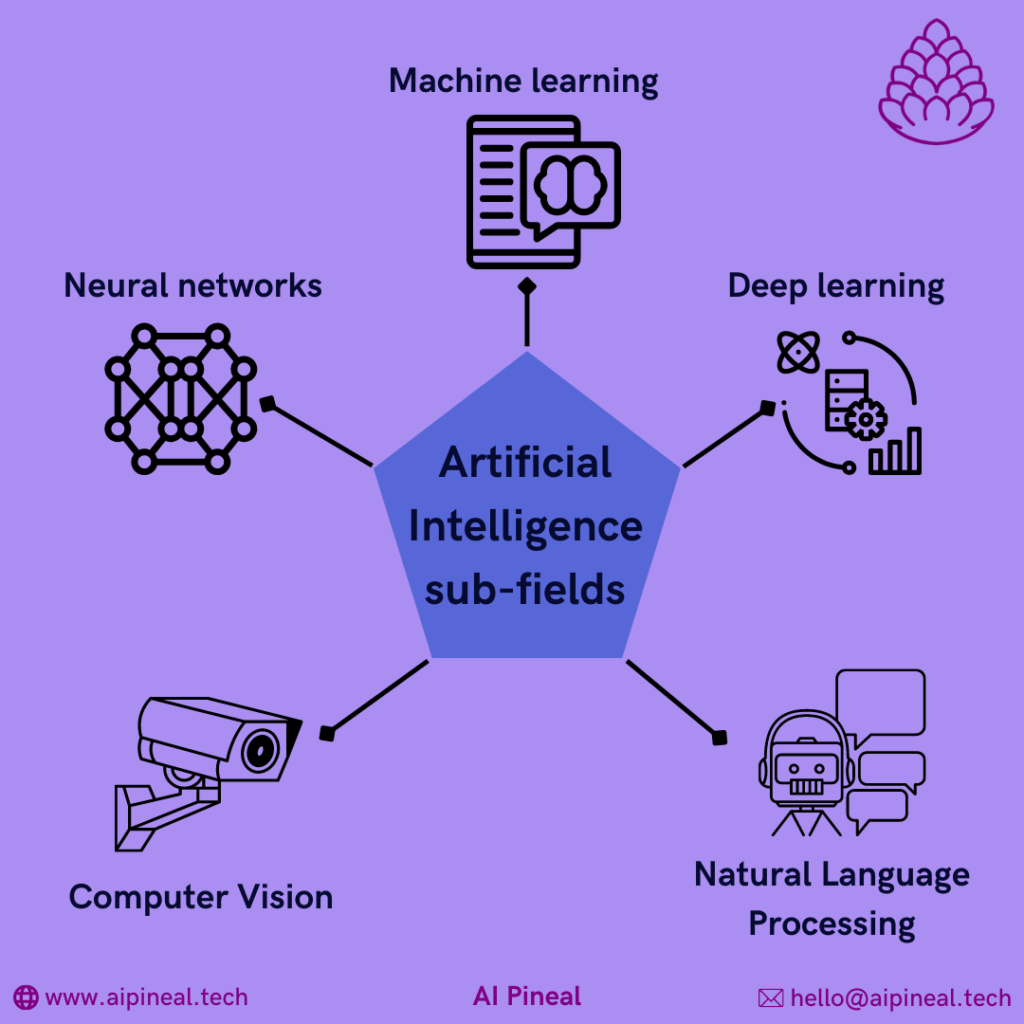
How does AI work using machine learning?
Without mentioning machine learning, any conversation on artificial intelligence would be meaningless. It is the fundamental concept, that gives artificial intelligence its “intellectual” quality.
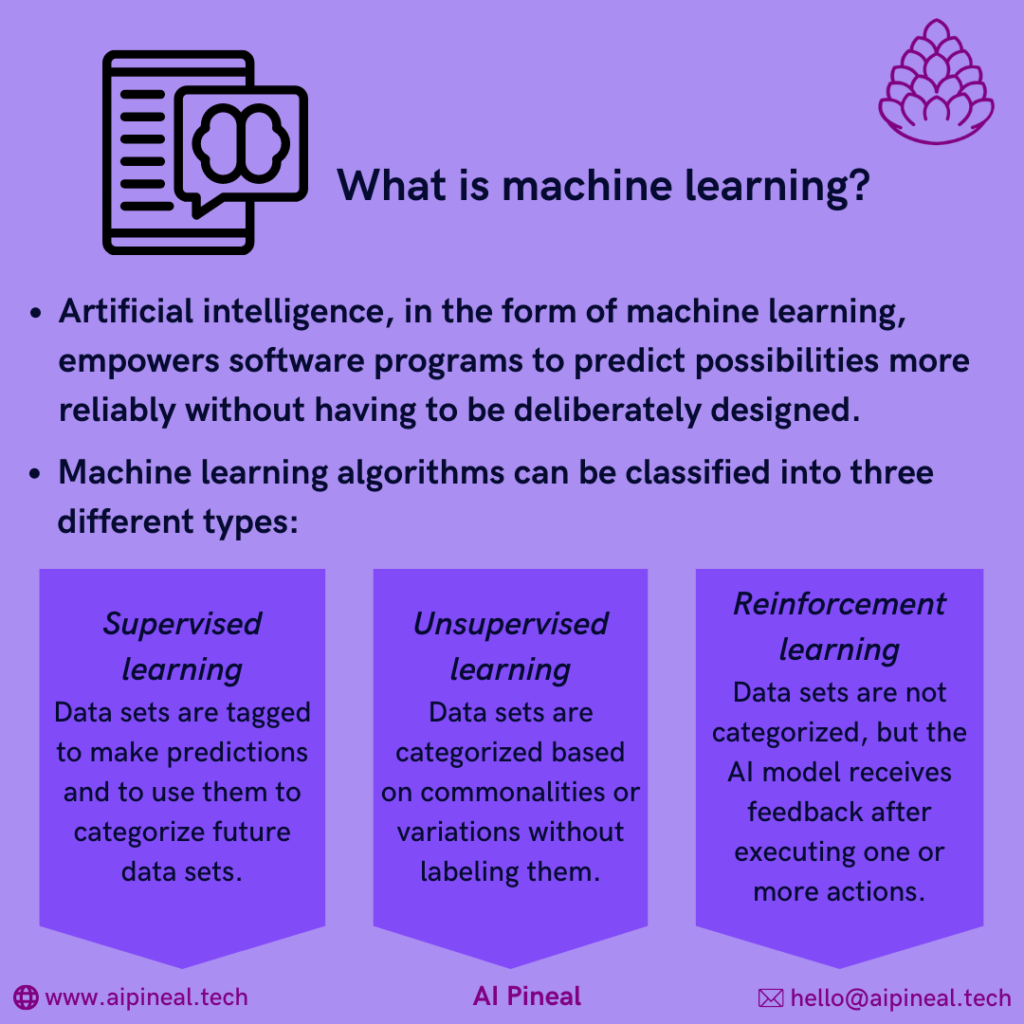
Artificial intelligence, in the form of machine learning, empowers software programs to predict possibilities more reliably without having to be deliberately designed.
Machine learning is the technology of enabling a computer to perform analysis without programming.
In simple terms, machine learning minimizes the requirement for thousands of lines of written code by providing computer data and using mathematical techniques to assist it in “understanding” ways to become incrementally better at a task without previously being specially designed for that purpose.
Machine learning teaches a computer to draw conclusions and make choices based on prior knowledge. Without relying on human insight, it recognizes patterns and evaluates historical information to determine the relevance of these pieces of data and arrive at a feasible conclusion.
Organizations can save time by using automation to analyze information and draw conclusions, which leads to wise and better decisions.
Machine learning algorithms can be classified into three different varieties:
Supervised learning: In supervised learning data sets are tagged to make predictions and to use them to categorize future data sets.
Unsupervised learning: Sets of data are categorized based on commonalities or variations without labeling them.
Reinforcement learning: Here, data sets are not categorized, but the AI model receives feedback after executing one or more actions.
Example: Machine learning is progressively being used in the pharmaceutical, biomedical, and medical sectors to speed up drug research and assist in the diagnosis of diseases, and comprehend medical data.
How does AI work using neural networks?
According to Britannica, a neural network is a computer program that operates in a manner inspired by the natural neural network in the brain.
Human neural units and artificial neural networks both operate on the same concepts. They are a collection of techniques that replicate the way a human mind operates, by identifying the correlation between numerous underlying parameters.
A neural network is a kind of machine learning that comprises connected, information-processing nodes (similar to neurons) that adapt to outside information and interact with one another.
To uncover interconnections and extract patterns from ambiguous data, the algorithm must make several runs through the information to identify relationships and make sense of unrecognized information. This approach analyses data several times.
The algorithm is trained, so that it has correctly detected the subject using a variety of learning approaches, such as positive reinforcement.
Example: The concept of Neural Networks has found application in developing trading systems for the finance sector. They also assist in developing processes such as time-series forecasting, security classification, and credit risk modeling.
What is deep learning?
One of the machine learning techniques is deep learning. It trains a program to categorize, interpret, and forecast the result by evaluating information through layering.
Artificial neural networks are techniques that are influenced by the structure and operation of the brain and are used in deep learning.
Computers are trained in what comes naturally to us using deep learning concepts. A computational model can be trained to do classification tasks using deep learning using data such as photos, text, or sound.
Deep Learning is growing in popularity as a result of the algorithms’ ability to achieve cutting-edge accuracy. Along with neural network structures, large labeled data sets are used to train these models.
A collection of input parameters are combined with each unit to create an output value, which is then transmitted to more cells in the network’s deeper layer.
Deep learning makes use of massive neural networks with multiple layers of processing units, getting the benefit of improvements in training methods and processing capacity to uncover complicated features in vast volumes of data.
To implement the identification of complicated and extract patterns within the data, deep learning systems frequently employ multiple layers, sometimes upwards of 100, and engage a significant number of units at each layer.
The activities that the computers perform are labeled as positive and negative as they learn, and this approach involves ongoing interpretation and reinforcement to advance.
Example: The deepfake, or producing a picture or video that so strongly resembles an individual that falsified media cannot be distinguished easily from the genuine thing, is one of the expanding application cases for deep learning.
What is computer vision?
Algorithms can now recognize, evaluate, and comprehend visual input thanks to the field of artificial intelligence known as computer vision.
Computer vision techniques attempt to comprehend a picture by dissecting it and examining various aspects of the object. This assists the algorithm in recognizing and studying from a collection of photos, enabling it to produce superior results based on prior observations.
The discipline of computer vision involves the creation of algorithms that let machines “see” and interpret digital pictures and videos. The objective of computer vision is to decipher data from visual resources and use it to resolve complex problems in the real world.
Computer vision uses deep learning and pattern recognition to identify what is present in a photo or video. Machines that can handle, evaluate, and comprehend images will be able to capture real-time images and videos and interpret their surroundings.
To analyze the information contained within an image, including the figures, tables, and photographs found in PDF files, the organization also takes the help of computer vision.
Example: Applications of this technology have already started to revolutionize sectors like healthcare and research & development. By analyzing patients’ x-ray scans with computer vision and machine learning, it is possible to diagnose patients more quickly.
What is NLP?
NLP is the study of how systems can analyze, comprehend, and evaluate languages.
Natural Language Processing (NLP), a part of artificial intelligence, is the capability of a system to comprehend spoken human language. Recognizing and interpreting natural speech is the goal of NLP, after which it will provide a conclusion.
The majority of NLP methods employ machine learning to extract information from human language. Once a program interprets what the human is trying to say, it reacts appropriately.
NLP examines, comprehends, and produces written or audio answers based on the natural languages that people speak. The end purpose of NLP is to make it possible for us to communicate with the technologies we use daily in a seamless manner by training computers to comprehend human language in context and to give reasonable answers.
Example: Natural Language Processing can be used in conversational AI systems like chatbots to interact with systems (and their human users) in both textual and spoken environments.
Ethical use of Artificial Intelligence
Although organizations may take advantage of a variety of capabilities of machine learning thanks to AI technologies, their use also presents moral dilemmas because, for better or worse, an AI model will repeat what it has already taught.
This presents a challenge since machine learning techniques, the foundation of many of the most cutting-edge AI products, are only as intelligent as the training data used to train them. Machine learning bias is a real possibility because people pick and select the information used to train AI systems. Therefore it needs to be supervised carefully.
Anyone who wants to incorporate AI techniques into functional, in-production applications must address morality when developing AI training procedures and work to eliminate prejudice. It becomes particularly relevant when applying AI technologies in Generative Adversarial Network(GAN) and deep learning applications, which are intrinsically inexplicable.
It will be difficult to create policies that will control AI because it consists of many distinct technologies that businesses utilize for multiple purposes and because policies may hinder the advancement and development of AI.
Another barrier to developing an effective AI policy is the technology’s tremendous growth. New applications of technology and technological advances can suddenly nullify existing laws.
AI in our everyday life
AI is deployed in several fields to provide data-driven suggestions and analysis of user behavior.
- To keep users engaged with the service and lengthen watch times, Netflix uses historical user data to suggest what films they would choose to watch next.
- Facebook intelligently recommends friends to tag based on facial attributes in their photographs by using historical user data.
- The next thing a person would enter in the search bar is predicted by Google’s predictive search algorithm using data from previous users.
- Amazon creates customized suggestions for consumers based on their past searches and purchases.
- Based on pattern recognition and attack retracing, AI systems can assist in identifying and combating cyberattacks.
- Website chatbots assist clients during off-peak and busy times, eliminating the barrier of scarce human resources.
- AI can read MRI images to look for tumors and other abnormal growths at an immensely quicker pace than doctors can, with a significantly narrower margin of error, thanks to computer vision and convolutional neural networks.
- AI-based language translation software offers language identification, translation, and subtitling services that can aid users in learning new languages.
Goals of artificial intelligence
The fundamental objective of AI is to make it possible for computers and other devices to carry out mental abilities, including solving a problem, reasoning, observing, and comprehension of human communication.
The ultimate goal is to develop a system that can behave thoughtfully, pick up new skills on its own, show, analyze, and make suggestions to its user.
A software program that can simulate human activity and employ human-like reasoning to solve complicated issues is the aim of AI science. AI systems use a wide range of methods, procedures, and various other technologies covered in the above sections to achieve this goal.
In conclusion, AI seeks to create software that can reason based on input and deliver an explanation based on output. AI will enable human-like engagements with computers and guide particular work decisions.
Purpose of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence’s purpose is to complement human abilities and assist us in making complex decisions that have broad implications.
It seems to have the ability to make it possible for people to have more fulfilling lives free from physical labor and to govern the intricate web of interconnected people, businesses, states, and countries in a way that benefits all humankind.
AI is now being called our “Final Invention,” a development that would produce ground-breaking products and services that, if successful, will drastically alter how we live our lives by reducing conflict, inequality, and misery.
Subscribe to our newsletter

